 |
 |
 |
RAID Implementation Types
 RAID 0+1
RAID 0+1
Requiring at least 4 drives, RAID 0+1 is a combination of, firstly, stripe (RAID 0) and then mirroring (RAID 1). Hence the term "RAID 01".
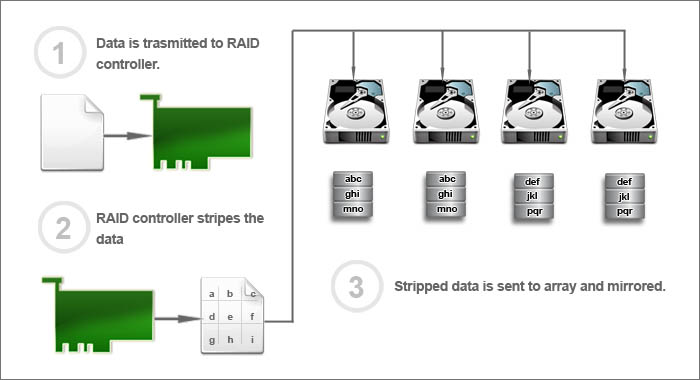
- The data is sent from server to RAID controller
- RAID controller will then stripe the data
- Then data set ABCD will be sent to array 1, and mirrored to array 2. Data set EFGH will be sent to array 3, and mirrored to array 4 and so on.
What happens during drive failure is that if a drive in "array 1" fails, that whole array is lost, due to the nature of RAID 0. However, "array 2" will still function as normal.
However, "array 2" will then function solely as a RAID 0. If any of the drives in "array 2b" fails, the system will go down and you will lose the entire array.
Another disadvantage here is storage capacity is halved, due to mirroring.



